- +91-7419192999
- info@pharmresbull.com
Pharma Research Bulletin – Pharmaceutical & Clinical Research Updates
Volume 4, Issue 2, 2025
Number of Articles - 4
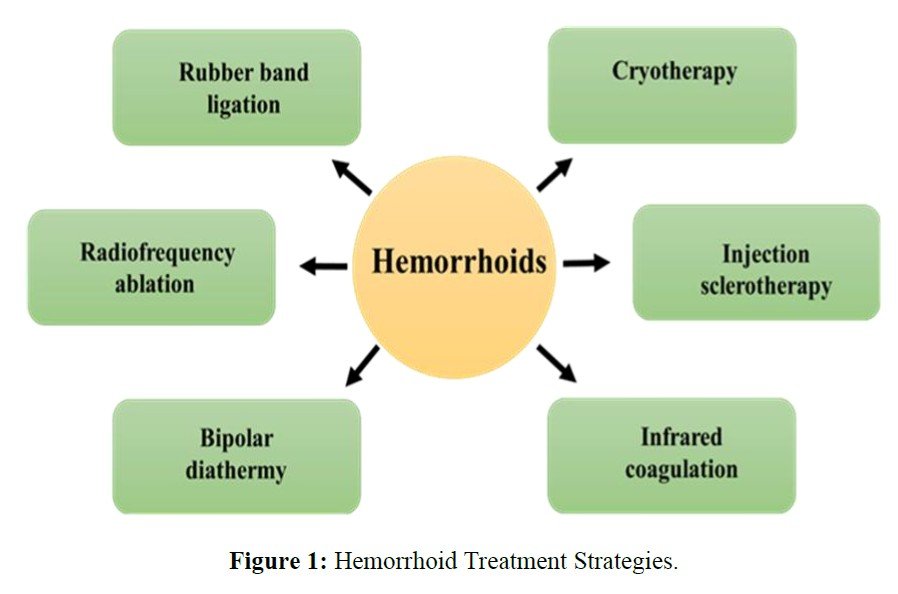
Hemorrhoid Management: A Holistic Exploration of Conventional Methods, Herbal Remedies and Clinical Research
Shilpi*, Vishakha Saini, Ashwani K. Dhingra.
*Ganpati Institute of Pharmacy, Bilaspur, Yamunanagar-135002, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Hemorrhoid Management: A Holistic Exploration of Conventional Methods, Herbal Remedies and Clinical Research
Hemorrhoids, a prevalent medical condition affecting a substantial portion of the global population, continue to pose challenges in terms of effective treatment strategies. This review article comprehensively examines diverse methods of hemorrhoid treatment, with a specific focus on herbal formulations and their clinical efficacy. In response to growing interest in natural therapies, the article thoroughly investigates hemorrhoid herbal treatment options. It highlights the utilization of various botanical agents, their traditional uses, and scientific evidence supporting their efficacy in alleviating hemorrhoidal symptoms. Special attention is given to formulations comprising plant-derived compounds, their mode of action, and safety profiles. The article synthesizes existing literature and clinical data to provide a comprehensive overview of conventional medical interventions alongside emerging herbal approaches. This evidence-based assessment aids in identifying gaps in current knowledge and areas warranting further research. In conclusion, this review article amalgamates a diverse array of hemorrhoid treatment methods, ranging from conventional medical interventions to emerging herbal formulations. As interest in holistic healthcare approaches grows, this review underscores the need for continued exploration of herbal treatments and their integration into conventional therapeutic paradigms.
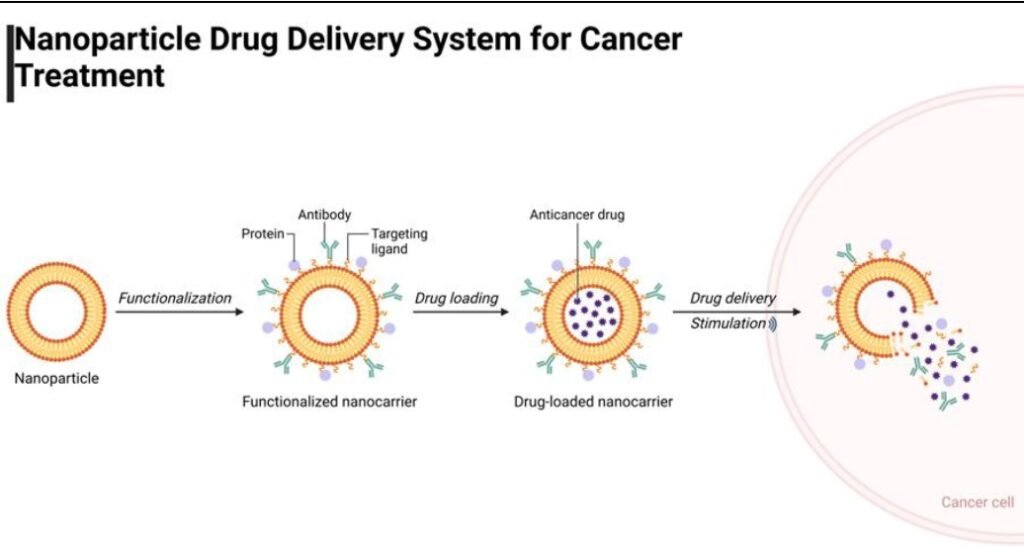
Advancements in Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications of Phytogenic Nanomaterials for Lung Cancer Management
Rupa Devi*, Dushyant.
*Global Research Institute of Pharmacy, Radaur, Yamuna Nagar-135133, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Advancements in Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications of Phytogenic Nanomaterials for Lung Cancer Management
Lung cancer is still a serious global health issue, and traditional therapy is hindered by drug resistance, toxicity, and non-selective activity against cancer cells. Phytogenic nanomaterials derived from plants provide a promising alternative since they are biocompatible, environmentally friendly, and show improved therapeutic efficacy. Nanomaterials such as metallic, polymeric, lipid-based, and carbon-based nanomaterials have highly effective anticancer activities by inducing apoptosis, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, targeted drug delivery, inhibition of angiogenesis, and immune stimulation. Phytogenic nanomaterials have shown efficiency in the treatment of lung cancer, such as targeted drug delivery systems, chemotherapy triggered by phytogenic nanomaterials, photothermal therapy, and gene therapy. Targeted drug delivery occurs by ligand-functionalization of nanoparticles, improving the specificity of therapy along with minimum systemic toxicity. Phytogenic nanoparticles also tackle drug resistance, increase chemotherapy, and allow the release of the drug in a controlled manner. Gold nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, and graphene oxide also offer photothermal therapy with local ablation of the tumor by heat. Gene therapies like RNA interference and CRISPR-Cas9 also increase therapeutic specificity. Apart from therapy, phytogenic nanomaterials are used in diagnostics and imaging, which improve the early diagnosis of disease by biomarker sensing and improved imaging contrast. Through continued research and development in the clinic, phytogenic nanomaterials have the potential to transform lung cancer therapy into personalized, efficient, and safer treatments.

Innovative SNEDDS for Targeted and Personalized Drug Delivery
Jasmeen Kaur*, Dushyant.
*Global Research Institute of Pharmacy, Radaur, Yamuna Nagar-135133, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Innovative SNEDDS for Targeted and Personalized Drug Delivery
Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SNEDDS) resulted in innovative approaches for improving the bioavailability and solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs. Conventional SNEDDS provide several benefits, such as improved dissolution and medication absorption rates. However, because of the less precise release of drugs at the location of action, traditional targeted drug delivery is limited. In recent times, additional focused advancements, such as innovative materials for new SNEDDS formulations, smart delivery systems, and personalized medicine, have emerged as a result of advances in treatment innovation. This chapter will discuss the most recent advances in SNEDDS, namely stimuli-responsive SNEDDS, which play a role in drug release in response to different environmental stimuli such as pH, temperature, as well as enzyme activity. Targeting ligands like peptides, nanoparticles, or monoclonal antibodies are used to deliver antineoplastic medications more effectively, minimising systemic adverse effects. The prospective use of artificial intelligence (AI) along with machine learning (ML) in developing SNEDDS formulations is underlined as a foundation for predictive modeling for stability augmentation, absorption, and personalisation. Furthermore, personalised SNEDDS accelerates the arrival of competent rapid care by incorporating pharmacogenomic data, making it relevant in providing prescription formulations to a single patient with enhanced efficacy and fewer side effects. The potential of hybrid SNEDDS, which combines nanoemulsions along with liposomes and polymeric nanoparticles to improve drug loading and also allow controlled release, is one of the prospects. Despite these gains, several challenges remain, including formulation stability, suitable scaling, as well as regulatory approval. However, with breakthroughs in research and multidisciplinary collaboration, the successful translation of novel SNEDDS into the clinic may pave the way for new-generation drug delivery systems that are more effective, patient-centred, and therapeutically relevant.

Addressing Schizophrenia in The Elderly: Advances and Best Practices in Geriatric Healthcare
Jagdeep Singh*, Dushyant, Jasvinder Saini, Shabnam, Amit, Shivani Singla.
*Global Research Institute of Pharmacy, Radaur, Yamuna Nagar-135133, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Addressing Schizophrenia in The Elderly: Advances and Best Practices in Geriatric Healthcare
Schizophrenia is a disabling and incurable mental illness that afflicts millions of people around the globe, including increasing numbers of older adults. The disease has been found to arise as a result of brain abnormalities caused by environmental, neurodevelopmental, and genetic causes. Symptoms are divided into three broad categories: negative symptoms (loss of interest and withdrawal of emotion), cognitive impairment (attention and memory dysfunction), and positive symptoms (delusions and hallucinations). Recent advances in medicine involve new treatment types, such as long-acting injectable, intranasal delivery of drugs, biomarker-targeted early diagnosis, and CYP2D6 enzyme profiling-based individually tailored treatment. Schizophrenia in older adults is particularly difficult to treat because of cognitive dysfunction associated with aging, comorbidity, and enhanced drug sensitivity. Personalized treatment involves reduced dosing of antipsychotics, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and systematic social support measures. Furthermore, novel digital rehabilitation methods like serious gaming and VR therapy are capable of increasing the cognitive functioning and overall well-being of geriatric schizophrenia patients. There needs to be a holistic, integrated approach for optimizing schizophrenia care among older patients through a mix of medical, psychosocial, and technology-oriented interventions to guide patient outcomes and caregiver support.

