- +91-7419192999
- info@pharmresbull.com
Pharma Research Bulletin – Pharmaceutical & Clinical Research Updates
Volume 5, Issue 1, 2026
Number of Articles - 11

Importance of Herbal Remedies in Neurodegenerative Disorders.
Devinder Kumar*, Rajesh Kumar, Sunil Dutt, Pankaj Kalia.
*Department of Pharmacology, Shiva Institute of Pharmacy, Chandpur, Bilaspur-174004, Himachal
Pradesh, India.
Abstract
Importance of Herbal Remedies in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Recent advancements in pharmacotherapy have renewed interest in herbal remedies as potential
therapeutic agents for the management of neurodegenerative diseases. This chapter highlights the significance
of herbal medicine in addressing complex systemic disorders, particularly neurodegenerative conditions.
Phytochemicals present in medicinal plants possess diverse biological activities and may exert neuroprotective
effects through multiple mechanisms, including neurogenesis, anti-inflammatory actions, and antioxidant
activity. Herbal medicine represents a holistic approach to healthcare, integrating therapeutic interventions
with dietary and lifestyle modifications to prevent disease progression. Moreover, herbal medicines are widely
accessible and cost-effective, making them especially valuable in resource-limited settings. These therapeutic
agents generally exhibit favorable safety profiles with fewer adverse effects compared to synthetic drugs,
despite challenges related to standardization and regulation. To fully harness the potential benefits of herbal
therapies for neurodegenerative diseases, it is essential to educate and empower patients and healthcare
professionals to engage in informed, collaborative decision-making. Future research should focus on
individualized treatment strategies, isolation and characterization of novel bioactive constituents, and well
designed controlled clinical trials. By effectively leveraging the therapeutic potential of herbal medicines,
individuals suffering from neurodegenerative disorders may achieve improved treatment outcomes and
enhanced quality of life.
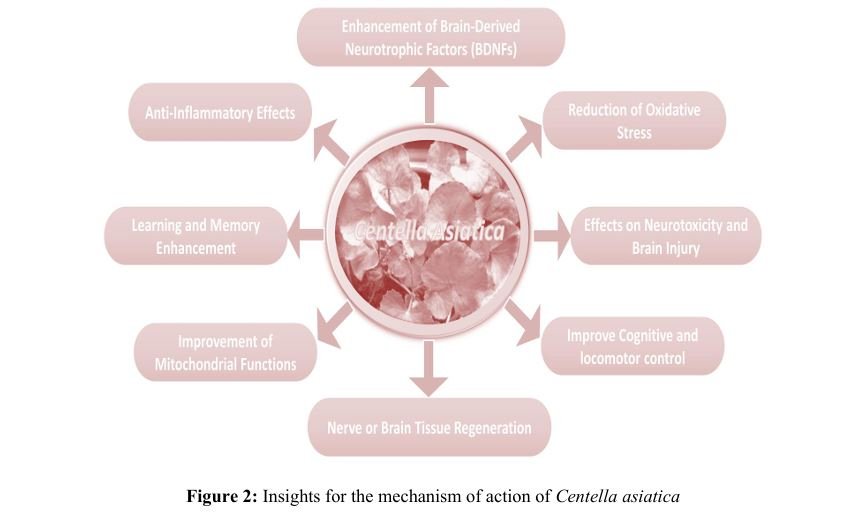
Centella asiatica (Gotu Kola): A Natural Solution for Neurodegenerative Disorders.
Arshi Khanam*, Rishabh Shrivastava Ronin, Parth Sharma, Ravina Yadav, Jigyasa Jai, Ritu M
Gilhotra.
*Gyan Vihar School of Pharmacy, Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur-302017, Rajasthan, India.
Abstract
Centella asiatica (Gotu Kola): A Natural Solution for Neurodegenerative Disorders
Diseases prevalent in an ageing society are often chronic and neurodegenerative. The growing recognition of the role of nutrition in healthy ageing has stimulated research into the therapeutic potential of traditional foods and medicinal plants. Centella asiatica (Gotu kola), a perennial herb native to Southeast Asia, has long been used in both Indian and Chinese traditional medicine and is now increasingly recognized for its neuroprotective potential against neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s diseases. Traditionally regarded as a brain tonic, C. asiatica has been shown to alleviate anxiety
and depression, while at the cellular level, it exhibits protective effects against oxidative stress and inflammation. Several studies have demonstrated that its plant-derived metabolites support neuronal growth,
survival, and repair by inhibiting apoptosis and neurotoxicity. These effects are attributed to bioactive compounds including asiaticoside, asiatic acid, madecassoside, and madecassic acid. The herb exerts its neuroprotective action through multiple disease-modifying pathways, including inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity, which reduces amyloid plaque formation in the brain. Preclinical investigations indicate that C. asiatica enhances cognitive function, improves memory, and promotes neuronal growth and regeneration. Its antioxidant properties enable the neutralization of free radicals, while its anti-inflammatory
effects suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines and microglial activation. Additionally, its anti-apoptotic activity
protects neurons by modulating key cell survival signaling pathways. In vivo studies further demonstrate the amelioration of cognitive deficits and the enhancement of synaptic plasticity. Although clinical evidence remains limited, available trials suggest improvements in cognitive performance and reductions in anxiety and
depression among elderly populations, underscoring its potential in the anagement of age-related neurodegenerative conditions. This chapter provides an overview of Centella asiatica, its major bioactive constituents, and their mechanisms of action, while highlighting the need for further rigorous research to validate and optimize the therapeutic use of these compounds in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders.
Ginkgo biloba in Neurodegenerative Disease .
Balram Chaudhary*, Charu Sharma, Manisha Lamba.
University Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra-136119, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Ginkgo biloba in Neurodegenerative Disease
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) are characterized by progressive neuronal loss resulting from
disrupted proteostasis, altered energy metabolism, chronic inflammation, synaptic dysfunction, and
pathological protein aggregation. These disorders share common features such as gliosis, neuronal atrophy,
and intracellular protein inclusions, although they differ in the specific neuronal populations affected and the
proteins involved. Hallmark pathological features include amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and
extensive cortical atrophy, particularly in the temporal and parietal regions. Among herbal therapeutics,
Ginkgo biloba has emerged as a widely used medicinal plant with potential benefits in multiple
neurodegenerative conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease,
multiple sclerosis, and ataxia. Its neuroprotective effects are primarily attributed to antioxidant, anti
inflammatory, vasoactive, and anti-apoptotic properties. Standardized Ginkgo biloba leaf extract contains
flavonoid glycosides and terpenoids, which act as the principal bioactive constituents responsible for free
radical scavenging, protection against hypoxia-induced neuronal damage, and inhibition of amyloid-β
mediated neurotoxicity. Owing to these properties, Ginkgo biloba extract is commonly used as a dietary
supplement to support cognitive function and mitigate age-related memory decline.
Exploring Liquorice’s Role in Neuroprotection: A Natural Ally Against Neurodegeneration.
Deepa Rani*, Vipin Saini1, Sarita Sharma, Madhu Vashisht, Tarun Nangia.
MM College of Pharmacy, Maharishi Markandeshwar (Deemed to be University), Mullana, Ambala,
Haryana-133207, India.
Abstract
Exploring Liquorice's Role in Neuroprotection: A Natural Ally Against Neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s, present
significant challenges due to their complexity and progressive nature. Recent research suggests that liquorice
(Glycyrrhiza glabra) may serve as a promising natural compound with neuroprotective potential.
Experimental studies have demonstrated that liquorice can protect neurons, primarily due to its bioactive
constituents such as glycyrrhizin, flavonoids, and saponins. This book chapter compiles the current
knowledge on liquorice’s therapeutic potential in neuroprotection, emphasizing its mechanisms of action,
safety profile, and potential as a complementary or adjunct therapy for neurodegenerative disorders. While
liquorice shows considerable promise as a natural neuroprotective agent, further clinical studies are required
to validate its efficacy and establish guidelines for safe and effective use.

Role of Jasminum sambac Extracts in Neurodegenerative Disorders.
Anjali, Anurag Bhargava, Jasmine Chaudhary, Rupa Devi, Mohit Kumar*.
Ch Devi Lal College of Pharmacy, Jagadhri, Yamuna Nagar-135003, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Role of Jasminum sambac Extracts in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Jasminum sambac, commonly known as Arabian jasmine, is renowned for its fragrant flowers and
medicinal properties. Recent research has highlighted the potential of Jasminum sambac and its extracts as
therapeutic agents against neurodegenerative diseases. Conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
disease involve progressive deterioration of neuronal structure and function, leading to cognitive deficits and
motor impairments. Jasminum sambac contains diverse bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, alkaloids,
saponins, and essential oils, which exhibit significant antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective
activities. These compounds have been shown to reduce oxidative stress, suppress neuroinflammation, and
inhibit apoptotic pathways, thereby protecting neurons from injury. Experimental studies suggest that
Jasminum sambac can enhance cognitive performance and memory, modulate key signaling pathways related
to neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and neurotransmitter regulation. Additionally, its ability to chelate
metal ions, inhibit amyloid-β aggregation, and preserve cholinergic function underscores its therapeutic
potential in neurodegenerative disorders. While preclinical findings are promising, comprehensive clinical
trials are needed to validate the efficacy and safety of Jasminum sambac in humans. These observations
emphasize the need for further research to explore its neuroprotective mechanisms and potential as a natural
therapeutic agent in neurodegenerative diseases.

Turmeric (Curcumalonga) Neurodegenerative Disorders.
Sukhwinder Singh, Punam Gaba*, Neelam Sharma, Mona Piplani, Shailesh Sharma.
Amar Shaheed Baba Ajit Singh Jujhar Singh Memorial College of Pharmacy, Bela, Ropar-140111, Punjab, India.
Abstract
Turmeric (Curcuma longa) Neurodegenerative Disorders
Turmeric is obtained from the dried rhizome of Curcuma longa L., also known as Curcuma
domestica Valeton, a perennial plant belonging to the family Zingiberaceae. It is widely cultivated in countries
such as India, China, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, and Peru. The rhizome exhibits a characteristic yellowish-brown
color due to the presence of curcuminoids, which are responsible for turmeric’s distinctive pigmentation.
Turmeric has a distinct aroma and a slightly bitter taste. The major bioactive constituent of turmeric is
curcumin, which accounts for approximately 50–60% of its total composition, along with volatile oils and
resins that constitute about 5%. Historically, turmeric has played a significant role in traditional medicinal
systems of East Asia, including Traditional Chinese Medicine and Indian systems such as Ayurveda. In India,
turmeric has been used for centuries to manage disorders related to the skin, upper respiratory tract, and
digestive system. The extensive historical use of turmeric in traditional healing practices has prompted modern
scientific investigations into its therapeutic potential. Recent studies have focused on its possible role in the
prevention and management of neurodegenerative diseases, which are characterized by the progressive loss of
structure and function of neurons, ultimately leading to neuronal death. Neurodegeneration is commonly
associated with factors such as chronic neuroinflammation, metabolic dysfunction, genetic predisposition, and
the accumulation of insoluble protein aggregates. Curcumin, the principal active component of turmeric,
exhibits notable neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing properties, suggesting its potential in slowing the
progression of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. However,
pharmacokinetic studies indicate that curcumin undergoes rapid metabolism and systemic elimination,
resulting in poor bioavailability, which remains a major limitation for its clinical application.
Plants and Their Extracts Against Neurodegeneration: Ginseng (Panax ginseng).
Arushi, Kavita Munjal*, Vinod Kumar Gauttam, Sheelu Singh.
Department of Pharmacognosy, Shiva Institute of Pharmacy, Bilaspur-174004, Himachal Pradesh, India.
Abstract
Plants and Their Extracts Against Neurodegeneration: Ginseng (Panax ginseng)
Ginseng, particularly Panax ginseng, has been highly valued in traditional medicine for its health
promoting effects. Recent preclinical and clinical studies have highlighted its promising neuroprotective
potential, mediated through multiple mechanisms of action. Among its diverse phytochemicals, ginsenosides
are considered the principal bioactive compounds responsible for these neuroprotective effects. They
contribute to the reduction of oxidative stress, inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and
suppress microglial activation, thereby mitigating neuroinflammation. Ginseng also influences key
neurotransmitter systems, including cholinergic, serotonergic, and dopaminergic pathways, which are critical
for cognitive function and mood regulation. Studies in Alzheimer’s patients have demonstrated improvements
in memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance following ginseng supplementation. The neurogenic,
anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities of ginseng further support its neuroprotective properties.
Nevertheless, further rigorous scientific investigation is required to fully validate its therapeutic potential and
identify possible side effects. This chapter provides a comprehensive overview of the physicochemical
properties, phytochemical composition, pharmacological actions, and clinical evidence of ginseng, with a
focus on its role in neuroprotection.
Role of Tinospora cordifolia Extracts in Neurodegenerative Disorders.
Madhu Vashisht, Anurag Bhargava, Akash Jain, Rupa Devi, Mohit Kumar*.
Ch. Devi Lal College of Pharmacy, Bhagwangarh, Jagadhri, Yamuna Nagar-135003, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Role of Tinospora cordifolia Extracts in Neurodegenerative Disorders
Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.), commonly known as Guduchi, has attracted significant attention for
its potential neuroprotective properties. Several studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Tinospora
cordifolia and its extracts in mitigating neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's,
which are characterized by progressive neuronal degeneration leading to cognitive decline and motor
dysfunction. The neuroprotective potential of Tinospora cordifolia is attributed to its rich repertoire of
bioactive compounds, including alkaloids, glycosides, steroids, and polysaccharides, which exhibit potent
antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects essential for preventing neuronal damage.
Experimental evidence indicates that Tinospora cordifolia can enhance cognitive function, reduce oxidative
stress, and suppress neuroinflammation. Moreover, it modulates critical signaling pathways involved in
neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity, further supporting its therapeutic potential. Additional mechanisms
include metal ion chelation, inhibition of amyloid-beta accumulation, and enhancement of cholinergic
function, all of which are relevant to neurodegenerative pathology. Despite promising preclinical findings,
clinical evidence remains limited, highlighting the need for rigorous clinical trials to confirm both efficacy and
safety in humans. These investigations are essential to establish Tinospora cordifolia as a viable natural therapy
for neurodegenerative diseases.

Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its extract for neurodegenerative disease.
Arpita, Karandeep Miglani, Aakriti Saini, Diksha Gulati*, Gagandeep Kaur.
Guru Gobind Singh College of Pharmacy, Yamuna Nagar-135001, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its extract for neurodegenerative disease
Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) is an aromatic evergreen shrub traditionally used for the
management of neurological and psychological ailments. Growing evidence highlights its broad
pharmacological potential, including antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antinociceptive, and
neuroprotective activities. Rosemary is rich in bioactive secondary metabolites that enhance memory and
cognitive performance and exert anxiolytic and antidepressant effects. Mechanistically, its neuroprotective
actions involve cholinesterase inhibition, modulation of dopaminergic and oxytocinergic signaling, regulation
of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, and attenuation of neuropathic pain pathways. Preclinical studies
demonstrate significant efficacy of rosemary extracts and constituents in animal models of neurodegeneration,
including amyloid β– and toxin-induced neurotoxicity, oxidative stress–associated neuronal damage, and
chemically induced cognitive impairment. Although preliminary clinical evidence supports these findings,
comprehensive clinical validation remains limited. This review highlights the therapeutic potential of rosemary
in neurodegenerative diseases and underscores the importance of integrating modern neuroscience with herbal
medicine to develop novel, safer neuroprotective strategies.
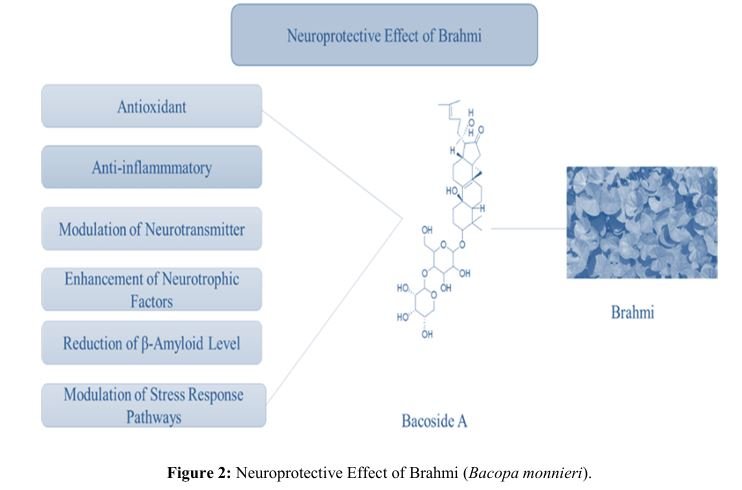
Brahmi and Its Extracts in the Administration of Neurodegenerative Syndromes.
Jyoti*, Minky Mukhija, Sonia Kamboj, Devkant Sharma.
Ch. Devi Lal College of Pharmacy, Jagadhri, Yamuna Nagar-135003, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Brahmi and Its Extracts in the Administration of Neurodegenerative Syndromes
Neurodegenerative syndromes are progressive disorders characterized by the irreversible loss of
neuronal structure and function, leading to cognitive decline, motor impairment, and reduced quality of life.
Despite advances in pharmacotherapy, current treatment strategies remain largely symptomatic and are often
associated with adverse effects, necessitating the exploration of safer and more effective alternatives. Bacopa
monnieri (Brahmi), a well-known medicinal herb in traditional systems of medicine, has gained increasing
scientific attention due to its neuroprotective potential. This review comprehensively summarizes the
pharmacological properties of B. monnieri, with particular emphasis on its bioactive constituents, including
bacosides, and their mechanisms of action in neurodegenerative syndromes. Experimental and clinical studies
suggest that Brahmi exerts antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cholinergic-modulating, and neuroprotective
effects, contributing to improvements in memory, cognition, and neuronal survival. The evidence presented
highlights the therapeutic relevance of B. monnieri as a promising candidate for the management of
neurodegenerative disorders and supports further research aimed at its clinical translation and formulation
development.

