- +91-7419192999
- info@pharmresbull.com
Pharma Research Bulletin – Pharmaceutical & Clinical Research Updates
Volume 3, Issue 1, 2024
Number of Articles - 5
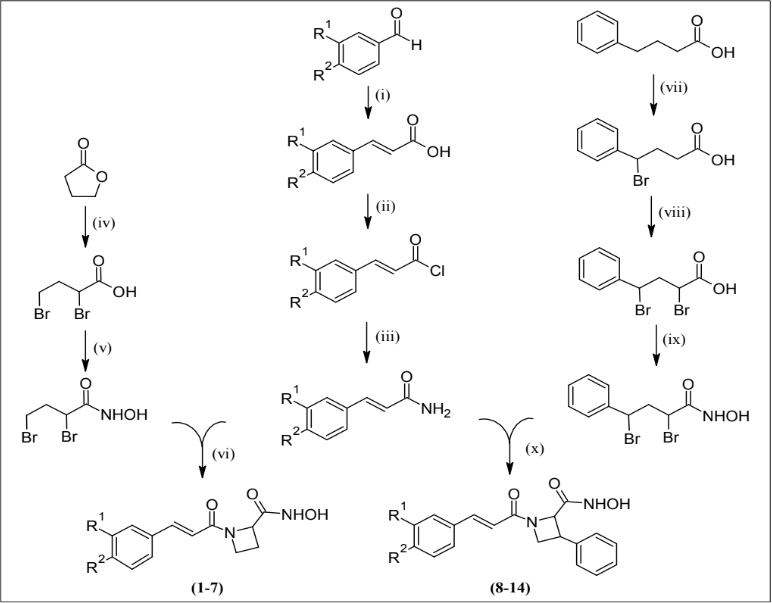
Design and Synthesis of A Newer Series of Caffeic Acid Analogs as Potential New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-1 (NDM-1) Inhibitors
Meenu Verma, Ajmer Singh Grewal*, Deepti Pandita, Viney Lather.
*Guru Gobind Singh College of Pharmacy, Yamunanagar, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Design and Synthesis of A Newer Series of Caffeic Acid Analogs as Potential New Delhi Metallo-β-Lactamase-1 (NDM-1) Inhibitors
New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1) constructing microorganisms are unaffected by all the
β-lactams together with carbapenems and pose an extreme risk to community wellbeing as they can simply
spread through horizontal gene transfer. The present work was planned to design, prepare and evaluate the
novel caffeic acid analogues as potential NDM-1 inhibitors. Docking studies were accomplished to explore
the binding interactions of the designed molecules in the active site of the NDM-1 protein. A newer series of
azetidine-substituted caffeic acid derivatives were synthesized using microwave irradiation and characterized
using FTIR and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Designed molecules showed appreciable hydrogen bonds with Asn220
and metal interactions with zinc ions in the active site of NDM-1. Compounds 1, 6, 9 and 14 showed powerful
in vitro antibacterial activities against Escherichia coli and compounds 4 and 13 showed potent antibacterial
activities against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The preliminary in silico results show an enormous potential for
these molecules to act as strong NDM-1 inhibitors.
Molecular Approaches and Significant Advances to Target Identification, Drug Discovery and Drug Development
Prabitha Prabhakaran, Sakshi Bhardwaj*, Dhivya Shanmugarajan, Sharath Chandra.
*Department of Life Sciences, Altem Technologies, Bangalore, India.
Abstract
Molecular Approaches and Significant Advances to Target Identification, Drug Discovery and Drug Development
Molecular pharmacology is a multidisciplinary field that explores how drugs interact with molecular
targets in biological systems to achieve therapeutic effects. It integrates molecular biology, biochemistry,
pharmacology, cheminformatics, and bioinformatics. Advances in biotechnology and molecular biology have
driven the discovery of new targets and the development of potent medications. The primary aim is to identify
optimal therapies by understanding drug interactions with receptors, enzymes, and transport molecules. Drug
design, based on knowledge of biological targets, involves rational approaches where molecules are tailored
to bind effectively. Computer-aided drug design (in silico) accelerates this process using methods like
molecular docking, dynamics, and pharmacophore modelling. The drug discovery and development process
includes early discovery, preclinical studies, clinical trials, FDA approvals, and post-marketing surveillance.
Computational techniques such as QSAR, ADMET profiling, and molecular modelling enhance target
identification and ligand optimization. High-throughput screening, aided by robotics and automation, enables
rapid testing of millions of molecules, leading to the discovery of therapies for cancer and neurological
diseases. Biotechnology advancements have enabled the development of monoclonal antibodies and gene
therapies, with technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 offering precise gene editing. Genomics and proteomics
accelerate target discovery by identifying disease-related genes and proteins, fostering personalized medicine
approaches. Molecular pharmacology continues to revolutionize drug design and discovery, providing new
opportunities for treating complex diseases and advancing precision medicine.

Plants Use in Human Zinc Deficiency: A Review
Nisha Grewal*, Ankit, Smita Narwal, Gurvirender Singh.
*Global Research Institute of Pharmacy, Radaur-135133, Yamunanagar, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Plants Use in Human Zinc Deficiency: A Review
Zinc is vital for human health, playing key roles in essential physiological processes like DNA
synthesis, immune function, and cellular activity. Despite its significance, zinc deficiency is a widespread
health issue impacting billions worldwide. While zinc supplementation is commonly used, incorporating plant-
based foods rich in phytochemicals presents an additional strategy to combat zinc insufficiency.
Phytochemicals, abundant in fruits, vegetables, and legumes, interact with zinc in intricate ways, influencing
how it is absorbed and utilized by the body. However, the relationship between plant compounds and zinc
absorption is complex, with some compounds facilitating absorption while others impede it. Understanding
these interactions is critical for optimizing dietary approaches to prevent zinc deficiency. Dietary factors,
especially in regions where cereal-based diets dominate and lack diverse plant foods rich in zinc, exacerbate
the prevalence of zinc insufficiency. Zinc deficiency can go unnoticed, posing challenges for diagnosis due to
its varied physiological effects. Plant-derived compounds like polyphenols, flavonoids, and saponins have
emerged as potential allies in addressing zinc deficiency, yet their effects vary depending on the context. While
zinc supplementation remains a common method, recent research suggests that plant-based compounds hold
promise in enhancing zinc absorption. This review delves into the history of zinc research, its physiological
impacts, absorption mechanisms, and therapeutic potentials. Furthermore, it explores the role of plants in
human zinc therapy, offering insights into future approaches to tackling zinc deficiency through plant-based
interventions. Collaborative efforts spanning various disciplines are essential to effectively address the global
burden of zinc deficiency and advance public health outcomes.
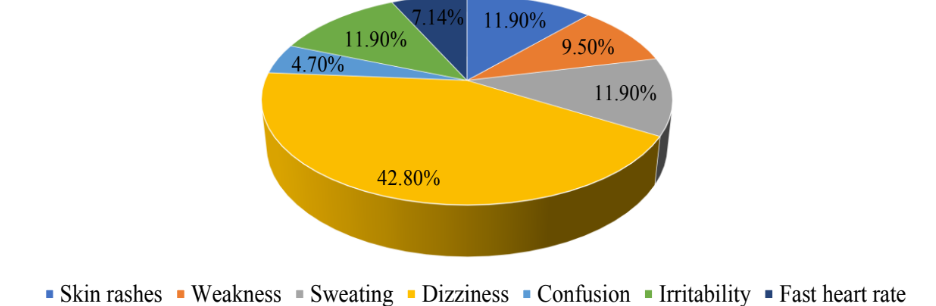
Targeted Monitoring of Adverse Drug Reactions Following Pregabalin and Nortriptyline Prescription Against Neuropathic Pain
Deepika Sharma*, Vishwadeepak Kimothi, Sameer Gupta.
*Chandigarh College of Pharmacy, Landran, Greater Mohali-140307, Punjab, India.
Abstract
Targeted Monitoring of Adverse Drug Reactions Following Pregabalin and Nortriptyline Prescription Against Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain is associated with lesions or illness affecting the somatosensory nervous system
(periphery or centrally). Clinically speaking, neuropathic pain is characterized by a pain that comes on
suddenly, lasts for a long time, or shoots, and by pain responses that are amplified in response to noxious or
non-noxious stimuli. The present study was designed to monitor various incidences of adverse drug reactions
(ADRs) associated with pregabalin (75 mg), and nortriptyline (10 mg) treatment of neuropathic pain either in
individual use or in combined form. The study enrolled 75 patients in three groups (each containing 25 patients)
suffering from neuropathic pain. The patients in different groups were treated with pregabalin (75 mg),
nortriptyline (10 mg) and pregabalin + nortriptyline combination (75 mg + 10 mg) for 120 days and monitored
for ADRs. Dryness of mouth, dizziness and sedation were the most common ADRs reported in 75 patients.
The other ADRs include tingling sensation, weakness, constipation, skin rashes, irritability dizziness, etc.
However, the patients treated with nortriptyline and pregabalin combination reported fewer ADRs as compared
to when used individually in the management of neuropathic pain.

Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Actions of Ginger: An In-Depth Review
Anmol Kaur, Shivani, Ajmer Singh Grewal*, Kumar Guarve.
*Guru Gobind Singh College of Pharmacy, Yamunanagar, Haryana, India.
Abstract
Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Actions of Ginger: An In- Depth Review
Zingiber officinale (generally known as ginger) is one of the utmost extensively employed herbs
and food flavouring agents. Z. officinale belongs to the family Zingiberaceae which has over 1200 species in
53 genera. Z. officinale is widely used in traditional medicinal systems to treat a wide range of illnesses. The
research includes its effects on cancer prevention, immune modulation, cardiovascular health, and pain relief.
Studies also highlight its potential in managing diabetes and gastrointestinal disorders. In the last few decades,
Z. officinale was extensively explored for its medicinal potential by innovative scientific methods and a
diversity of bioactive molecules were derived from this plant and investigated pharmacologically. The present
study is collective information concerning the phytochemistry and pharmacological activities of the herb Z.
officinale.

